Q) How do computers understand and store the data?
→ Computer machines are composed of digital memories that store information in bits (binary digits). The bit represents a logical value, which corresponds to a two-state device. These states are often represented as 0 or 1 and “true/false”
In programming languages, like C language, it is possible to declare variables in order to store numeric data in the computer memory. The number of bits that represent integers (Int) data type can change according to the computer architecture, or processing, and the compiler. In a 16-bit machine, the size of an integer is 2 bytes, but in a 32-bit or 64-bit machine, the size is 4 bytes.
But,
Q)What are bytes?
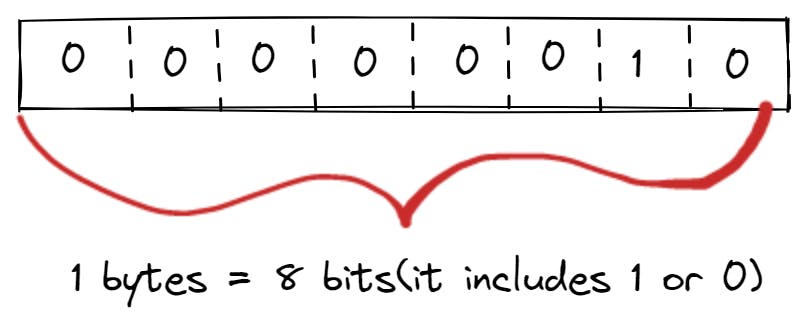
→ A byte is commonly known as a group of 8 bits.
below is an image
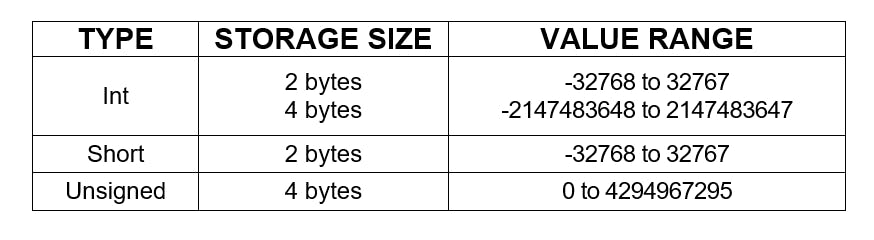
There are three data types that allow storing integers values: int, short and unsigned. According to the storage size of each data type, a short integer is represented by 16 bits, while an unsigned integer is represented by 32 bits. With the purpose of using enough computer memory, each data type is used according to the value range of the stored numbers. The values range of integers are shown in the following table :
signed(short) Int hold both positive and negative values
unsigned Int hold only positive values
Supposing there is a java program — compiled in 64-bits — where will be declared an integer variable with a value of 10 as shown below:
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int A = 10;
System.out.println("the value of a is " + a);
}
}
Output:- the value of a is 10.
Let's see how it is internally working. First, the computer assigns the memory for variable. Then var A will be converted into decimal form and transferred into bits.
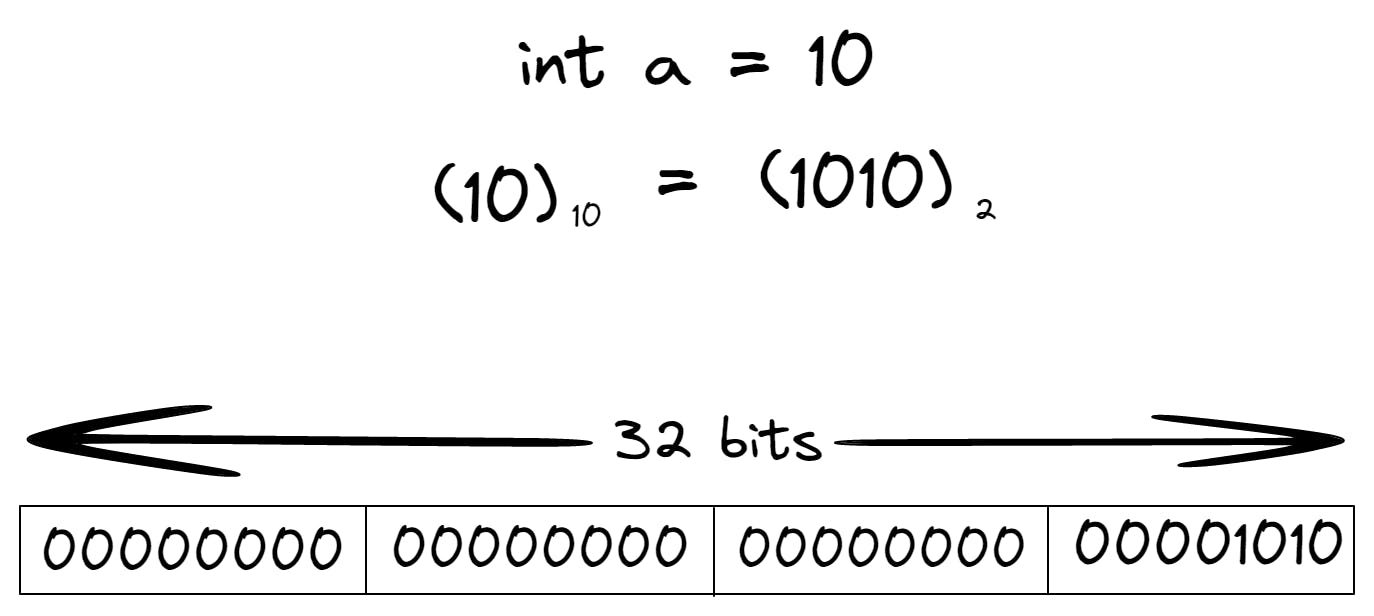 Illustration of the storing of an integer, with a size of 4 bytes, in the computer memory
Illustration of the storing of an integer, with a size of 4 bytes, in the computer memory
A binary with a static size represents an integer within a value range determined. For unsigned binary numbers, this value range goes from 0 to the value obtained when all digits are equally to “1”. With 2 and 4 bytes, the maximum integer value obtained by a binary of 2 and 4 bytes is shown below:
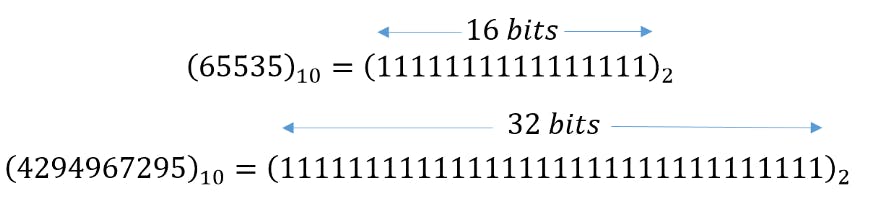 Maximum integer values were obtained from 2 bytes (16 bits) and 4 bytes (32 bits).
Maximum integer values were obtained from 2 bytes (16 bits) and 4 bytes (32 bits).
It means that their value range is determined by the following mathematical notation:
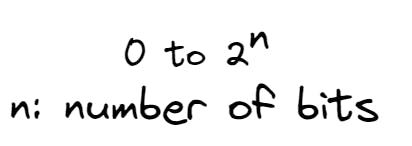
This is the way computer memory interprets unsigned integers. But for signed integers, in which a dash (“-”) is written before the number when it is negative, it changes.There are some methods to represent negative numbers from a binary.
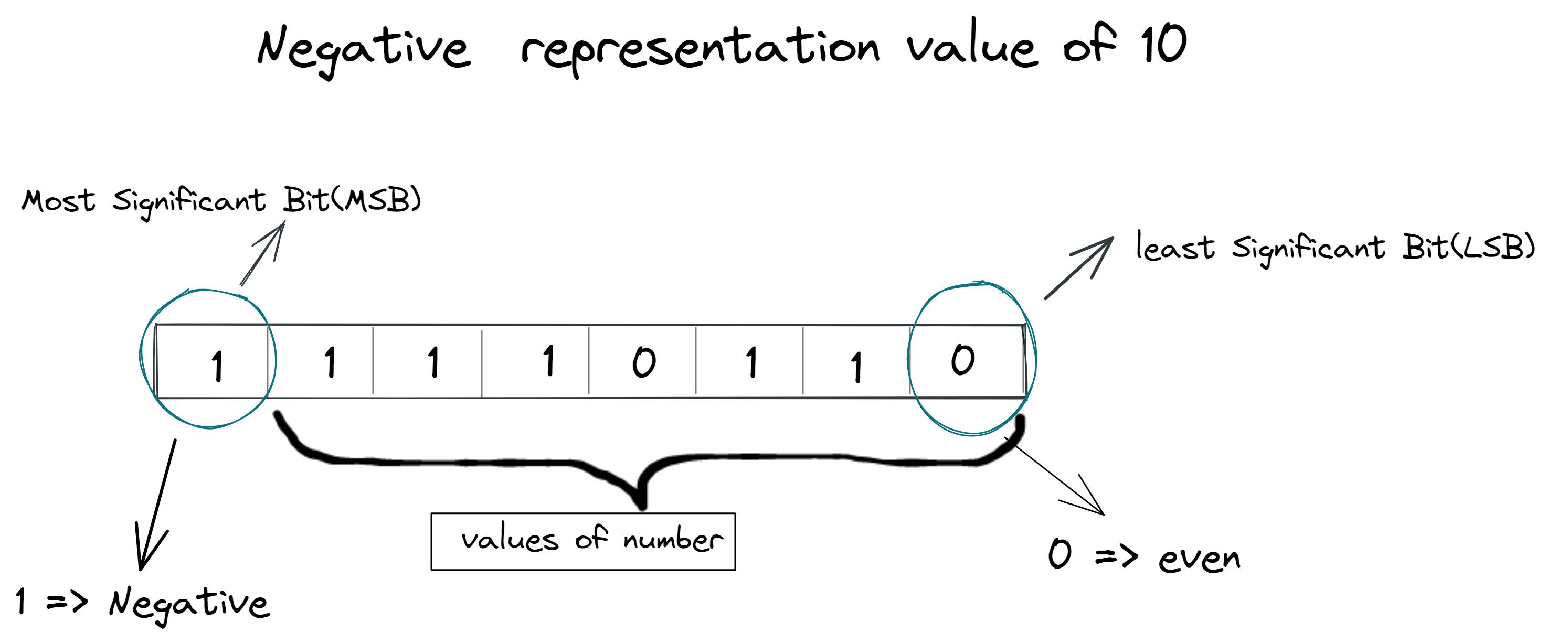
Let's see how the Negative number is stored
SIGNED BINARY NUMBERS
An integer number is identified as positive or negative if it has or does not have a dash before. In other words, this number only has of two-states. Each state can be represented through a bit of the binary number. This is called as Most Significant Bit (MSB): if the number is positive, this has a value of 0, but if the number is negative, the bit is 1. The entire number is called a signed binary number.
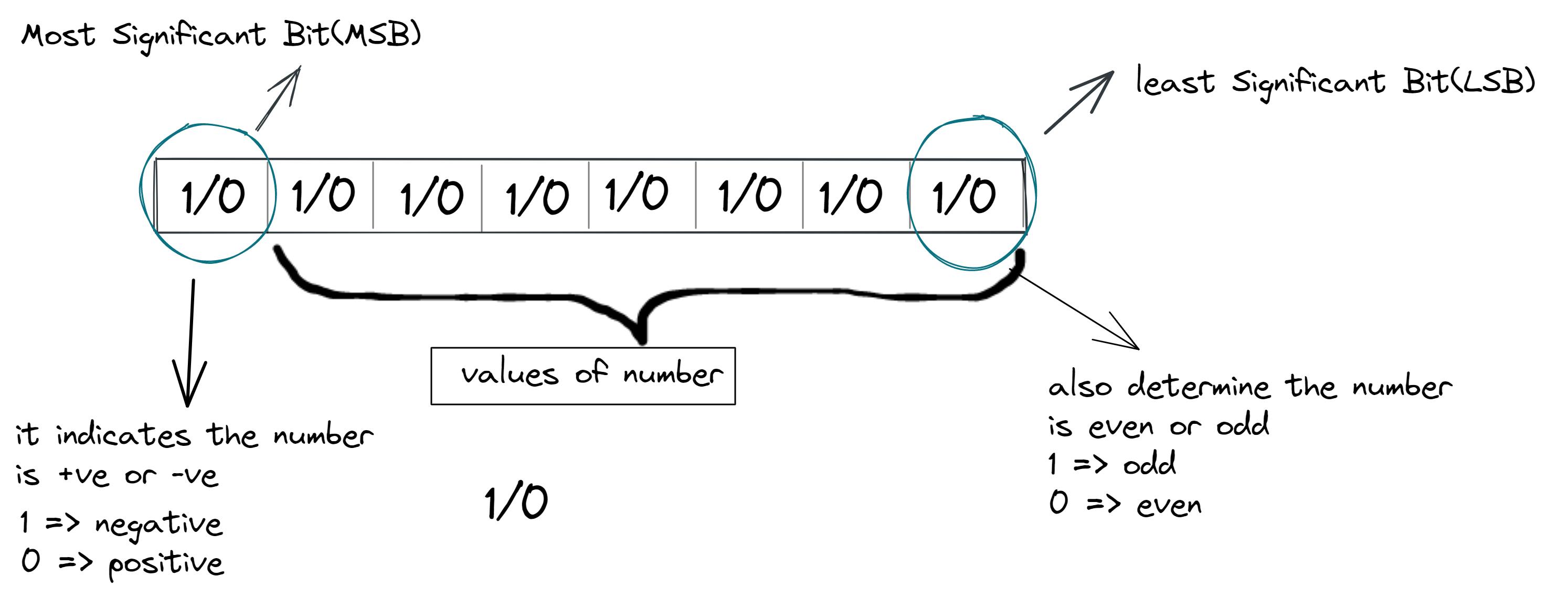
here is example:-
With the possibility of representing negative numbers, the value range of positive numbers is reduced. This happens because the number is obtained from (n-1) bits. Therefore, the value range is expressed by the following mathematical notation:
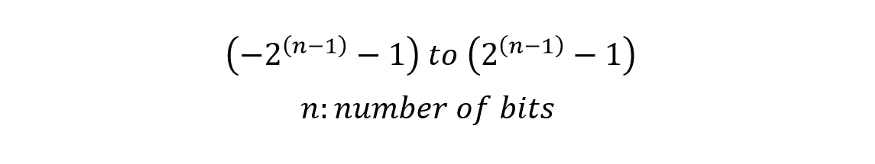
Through the Most Significant Bit, it is obtained a positive and negative zero (0 and -0). Negative zero does not exist in the decimal numeral system.
Steps to calculate the Negative value of any number
Step1: convert into binary form (Base2)
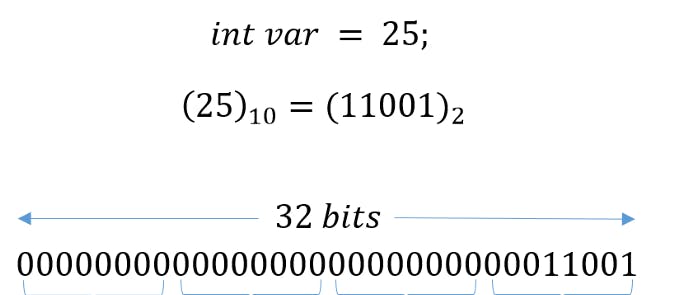
Step2:ONE’S COMPLEMENT.
Reverse the bits 1 => 0 and 0 => 1) It is a method that represents a negative number by inverting the values of bits of the number magnitude. Since the value first bit (also called the sign bit) of the positive number is 0, when the inversion is done, this first bit is equal to 1 to indicate a negative number. The sign binary number obtained from the inversion is called complement. The following image is an example of the process of inversion with one’s complement:

Step3:TWO’S COMPLEMENT
It is a method to represent negative integers, similar to one’s complement. It also inverts the magnitude of the negative number but, then, it is added one (+ 1) to the complement number [4]. It has a sign bit that allows indicating if a number is positive or negative.

For the reasons explained above, this method is used by computer memory to store signed(-ve)integers.
Range of Numbers
total unique numbers we can store in 1 byte is 256(2^8). In one bit we can store 2 values i.e either 1 or 0. The actual number is stored in bits = N -1(because the first bit is MSB). In 1 byte actual number that will be stored is 7 bits. The total we can make from 7 bits is 128. So 128 from the negative side and 128 from the positive side. so in the range of -128 to 128, it also contains 0.if we count the total it should be 257, not 256. for solving this problem we have to reduce the positive side number i.e 127. The final range of 1 byte of numbers is -128 to 127.
Range formula for N bits
-2^(n-1) to (2^(n-1)-1)
Do Like save and comment if you like it
